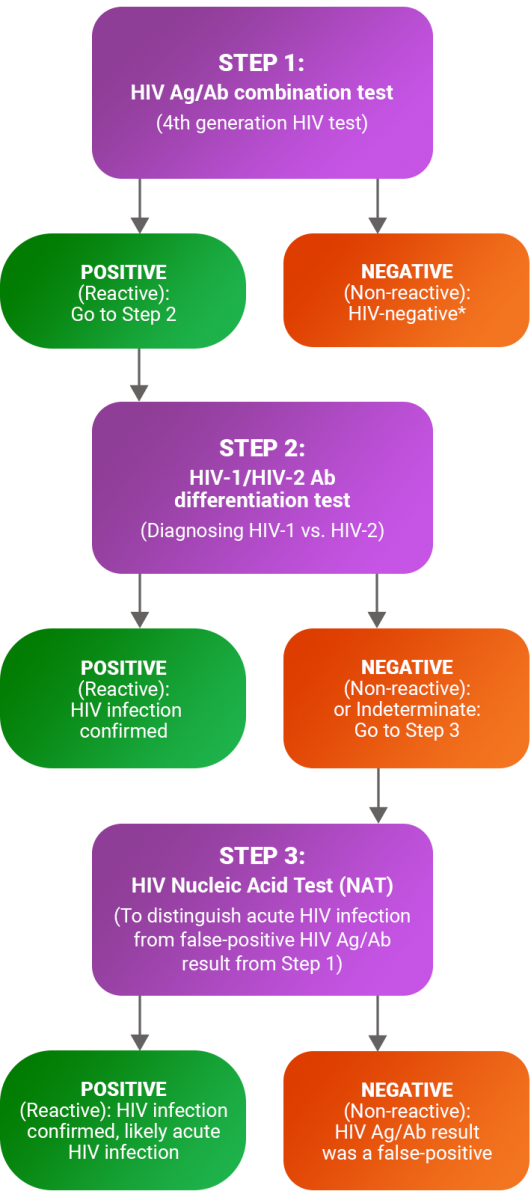
Routine screening for HIV infection is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) at least once for all adolescents and adults, and more frequently for persons who engage in activities where HIV may be transmitted. This algorithm outlines the initial and confirmatory laboratory-based tests to be ordered for HIV infection screening and diagnosis.
Abbreviations
- Ab = antibody
- Ag = antigen
Note:
* If suspicion of acute HIV infection or high-risk exposure within the last 2-4 weeks, check HIV RNA.
About the Tests
HIV Antigen/Antibody Combination Test
The HIV Ag/Ab combo test is an immunoassay that detects HIV in the blood by identifying either the HIV-1 p24 antigen or HIV antibodies. P24 is a viral protein which appears in the blood sooner than antibodies. This Ag/Ab test can detect HIV infection earlier than Ab-only tests, and generally a week after HIV RNA is detectable, or about 17 days after infection.
HIV-1/HIV-2 Antibody Differentiation Test
The HIV-1/HIV-2 Ab differentiation test is an immunoassay that is used both to confirm HIV infection (if the screening Ag/Ab test is positive) and to distinguish between HIV-1 and HIV-2. Results may show infection with HIV-1, HIV-2, both, or neither. Laboratory-based HIV-1, HIV-2 Ab tests can detect infection 22-25 days after infection.
HIV Nucleic Acid Test (NAT)
HIV NAT is an RNA test used to improve detection of early HIV infection. HIV-1 RNA levels are generally detectable approximately 10 days after infection. Available NAT tests in the U.S. are usually specific to HIV-1, the most common variant. HIV-2 NAT tests may be available through specialty laboratories. This test is generally considered to be too expensive to be practical for initial screening.
Resources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Association of Public Health Laboratories. Laboratory Testing for the Diagnosis of HIV Infection: Updated Recommendations. June 27, 2014.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Association of Public Health Laboratories. 2018 Quick reference guide: Recommended laboratory HIV testing algorithm for serum or plasma specimens. January 27, 2018.
- National HIV Curriculum. Acute and Recent HIV Infection. September 19, 2020. Offers 1.5 CE.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Implementing HIV Testing in Nonclinical Settings: A Guide for HIV Testing Providers. March 2, 2016.
Source
Modified from CDC 2014 and 2018 by John Nelson, PhD, CPNP, Susa Coffey, MD, and Nicole Mandel from the AETC National Coordinating Resource Center, February 2021.