
Assessment, treatment, and follow-up recommendations for people with known or potential exposures to HIV and other infections. Health care providers should evaluate persons rapidly for nPEP when care is sought ≤72 hours after an exposure that presents a substantial risk for HIV acquisition.
Risk Assessment
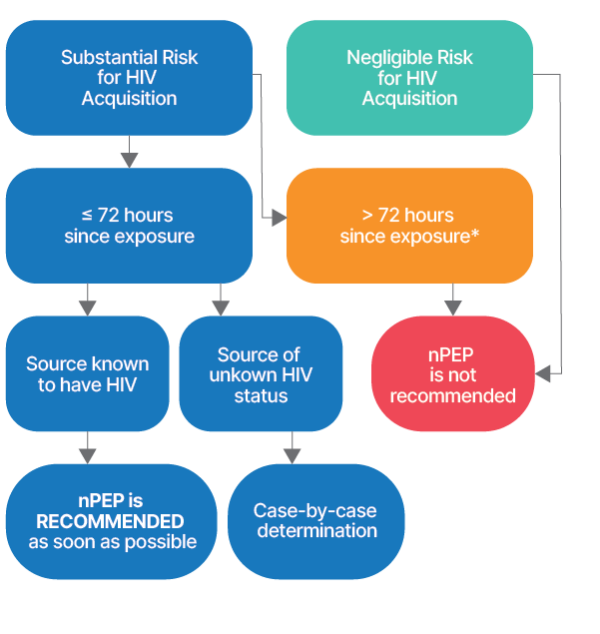
Substantial Risk for HIV Acquisition
Exposure of: vagina, penis, rectum, eye, mouth or other mucous membrane, non-intact skin, or percutaneous contact
With: blood, semen, vaginal secretions, rectal secretions, breast milk, any body fluid that is visibly contaminated with blood
When: the source is known to have HIV
Negligible Risk for HIV Acquisition
Exposure of: vagina, penis, rectum, eye, mouth or other mucous membrane, non-intact skin, or percutaneous contact
With: urine, nasal secretions, saliva, sweat, tears (if visible blood, see “Substantial Risk for HIV Acquisition”)
When: regardless of the known or suspected HIV status of the source
Laboratory Assessment
- HIV Ag/Ab: Rapid (point of care) 4th generation (Ag/Ab) test is preferred, but if not available, a rapid Ab test or a non-rapid lab-based HIV test should be done. If non-rapid testing is done, start nPEP immediately and arrange follow-up in 1-2 days for HIV results.
- If the rapid HIV test is reactive (positive), the person should NOT be given nPEP, but should be offered immediate antiretroviral therapy (before being discharged) and should be linked to ongoing HIV care.
- Gonorrhea (GC) and chlamydia (CT) NAAT: Offer tests according to sites of sexual contact (e.g., swabs for oropharyngeal, rectal, vaginal sites; urine for urethral site).
- For post-sexual assault patients, STI testing should be considered; empiric treatment should be provided whether or not STI testing is done.
- Syphilis test: RPR/VDRL or treponemal test
- For post-sexual assault patients, STI testing should be considered; empiric treatment should be provided whether or not STI testing is done.
- Urine pregnancy test for persons at risk of pregnancy
- Serum creatinine, ALT, AST
- Hepatitis B sAb, cAb, Ag
- Hepatitis C Ab
Treatment
Adults and adolescents (≥ 13 years) see below. Regimens for children and people with reduced renal function are also available.
If rapid HIV testing result is negative (non-reactive), or if lab-based test is sent and is pending, offer nPEP and as appropriate, STI treatment, emergency contraception, hepatitis B prophylaxis, and HPV vaccination:
HIV prophylaxis: Administer first dose of nPEP on site as soon as possible after a negative rapid HIV test result is obtained or a non-rapid HIV test is sent.
- Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)/emtricitabine (FTC) (Truvada) 300/200 mg + dolutegravir (Tivicay) 50 mg – 1 tablet of each PO daily x 28 days (2016 Guidelines)
- Many providers prescribe tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)/FTC (Descovy) in place of TDF/FTC, and bictegravir in place of dolutegravir. Bictegravir is available as a coformulation with TAF/FTC (bictegravir/TAF/FTC, Biktarvy).
- If client is in the first trimester of pregnancy OR may become pregnant within the next 28 days: TDF/ FTC (Truvada) 300/200 mg 1 tab PO daily + EITHER dolutegravir (Tivicay) 50 mg 1 PO daily OR raltegravir (Isentress) 400 mg 1 tab PO twice a day.
- The use of dolutegravir at conception and in very early pregnancy has been associated with a small, but not statistically significant, increase in the risk of fetal neural tube defects (see package insert).
- Truvada should not be used for those with CrCl less than 60 mL/min; an alternative regimen must be used in those circumstances.
Sexually transmitted GC, CT, and trichomonas empiric treatment: offer to all with sexual exposures (oral, vaginal, or rectal exposures)
- GC: Ceftriaxone (500 mg IM x 1 [1,000 mg IM for persons weighing ≥ 150 kg]) is the recommended treatment for GC and should not be substituted with another antibiotic unless there are clear contraindications (see CDC 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines for alternative).
- CT: doxycycline 100 mg PO twice/day x 7 days (or if pregnant, azithromycin 1 gram PO x 1)
- If risk of vaginitis: metronidazole 2 grams PO x 1
- Emergency contraception: Offer to persons at risk of pregnancy with a negative pregnancy test.
- Hepatitis B prophylaxis: Administer 1 dose of hepatitis B vaccine to persons not previously vaccinated or incompletely vaccinated. If the exposure source is available for testing and is HBsAg positive, unvaccinated exposed persons should be given both hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin during the initial nPEP evaluation. Follow-up dose(s) of hepatitis B vaccine should be administered according to the vaccine prescribing information. Previously vaccinated exposed persons who did not receive postvaccination testing should be provided a single hepatitis B vaccine booster dose.
- Prophylaxis against hepatitis C is not recommended.
- HPV vaccination: For those aged 9 to 45 years inclusively, offer HPV vaccination dose if not adequately vaccinated previously (see Gardasil package insert).
Patient Education
- Possible nPEP drug side effects: nausea, GI upset, ;headache, myalgias
- Possible nPEP drug interactions: antacids, calcium, iron supplements
- Stress the importance of adherence to the nPEP regimen for 28 days, without interruption
- For those with ongoing risk of HIV infection, offer PrEP initiation immediately after completion of the 28-day course of nPEP
Follow-up
- Follow-up should be scheduled at 72 hours and 4-6 weeks after initiating nPEP
- HIV Ag/Ab test after initial non-reactive test
- Syphilis test at 4-6 weeks and 3-6 months after exposure
- HBV and HCV serology tests at 6 months after initial non-reactive test if susceptible at baseline
References and Resources
- CDC. Announcement: Updated Guidelines for Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis after Sexual, Injection-Drug Use, or Other Nonoccupational Exposure to HIV - United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016 May 6;65(17):458. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6517a5. PMID: 27149423.
- See Table 5 for prescribing information for adults with renal disfunction and children.
- AETC NCRC. Medication Assistance Programs for HIV prevention and treatment.
- Contact the free National Clinician Consultation Center (NCCC) PEPline at 888-448-4911.
